Optimization ideas
Map the independent variables of the NIOSH lifting equation to dimensions of the elderly shopping trolley were. Ergonomic analysis of the actions involved in the shopping activity using 3D simulation software. Jack 8.0.1 and Rhino 7 were used as tools, to model and import the shopping trolley and the digital human body, construct the shopping activity simulation scenario, and perform dynamic simulation of the shopping activity to achieve the operation and analysis of the actions. The simulation process comprises three evaluation modules: Lower Back Analysis (LBA), NIOSH lifting analysis (NLA), and Reach Zones Analysis (RZA). The optimal values of the dependent variables are obtained through analytical equations and constrained optimization methods. The effectiveness of the optimized NIOSH lifting equation in reducing human fatigue and enhancing user experience is analyzed and verified in conjunction with ergonomics theory. Figure 2 illustrates the process of optimising the design
Optimization methodology
In the preceding section, we primarily divided the optimization process into five steps: research, acquisition of simulation preset parameters, optimization analysis using the NIOSH lifting equation, constrained optimization, and simulation comparison. These five steps constitute a systematic and comprehensive framework for design optimization, employing scientific methodologies to ensure that the design of shopping carts for the elderly aligns with ergonomic principles and effectively enhances their shopping experience. Below is a detailed elaboration of each step in the article.
(1) Research: This step is divided into three subprocesses. Through research on the anthropometric dimensions of the elderly, shopping behaviors, and existing products, we aim to understand the underlying purposes of user behaviors and the deficiencies of current products, selecting the target for optimization analysis. Based on the psychological and physiological needs of the elderly, suggestions for product operation, design, and color are proposed to enhance the user experience.
(2) Acquisition of Simulation Preset Parameters: Force analysis is conducted on the target object, simplifying structures that do not influence the outcome. Subsequently, a simulated scenario is constructed based on the shopping behaviors of the elderly to acquire simulation preset parameters, which serve as comparison benchmarks for later product optimization validation.
(3) NIOSH Lifting Equation: The meanings of the independent and dependent variables in the equation are analyzed, with the mapped meanings of the independent variables in the shopping process being extracted. The implications and trends of the dependent variables are also analyzed.
(4) Constrained Optimization: Combining constrained optimization methods, the corresponding values of the independent variables are derived through analysis of the dependent variables. Finally, by regressing to the mapped meanings, the optimal dimensions for shopping carts for the elderly are obtained.
(5) Simulation Comparison: The optimal dimensions derived from the above analysis are compared with the simulation preset parameters. A comparative analysis is conducted before and after optimization to verify the effectiveness of the NIOSH lifting equation in optimizing shopping carts for the elderly.
Simulation environment setup
The factors affecting shopping behavior of the elderly are mainly human, machines and environment21. Using JACK simulation software to simulate shopping activities, five action modules were designed for grasping, pushing, pulling, picking up and placing commodities. A digital human body model was established based on the anthropometric data of 61–70-year-olds in GB/T 10000-2023, as presented in Table 1. According to the market research, the size range of existing shopping trolleys for the elderly is 260 mm–650 mm \(\times\) 350 mm–500 mm \(\times\) 860 mm–960 mm, with basket sizes ranging from 200 mm–480 mm \(\times\) 250 mm–420 mm \(\times\) 400 mm–550 mm. The application of Rhino software to on the market is the most widely used one of the senior citizen shopping trolley 1:1 modeling, the model is simplified without affecting the analysis results to improve the simulation efficiency, as shown in Fig. 3. Since bending is greater below waist height, the damage to the human body caused by the action of picking up commodities from the bottom of the shopping trolley was mainly analyzed and simulated. The created digital human and the simplified model were placed into the simulated shopping environment, and the human action posture was adjusted using the human control window. The action animation of the shopping activity was created with five action modules of retrieve, push, putting, grasping and pulling, as shown in Fig. 4 (P5 of female as an example)
In both the pushing and pulling postures, functional hand height (axis of grip) affects the inclination between the human hand and the pull rod. The paper assume an angle of \(65^{\circ }\) between the lever and the ground when pushing the shopping trolley. The angle between the lever and the ground when pulling the shopping trolley needs to be adjusted according to different heights. For a P5 female, the proposed angle between the lever and the ground when pulling the shopping trolley is \(35^{\circ }\). Figures 5 and 6 show the force analysis of points A, B, and C, which represent people, objects, and wheel force points. F1 and F3 are required to overcome the force of gravity upwards, while F2 and F4 are required to overcome the friction force from the ground, respectively. This the paper selects home shopping trolley wheels made of PU material, which have a coefficient of rolling friction on the ground of 0.02.
$$\begin{aligned} & F_{1}=x_{1} G / x_{2} \end{aligned}$$
(1)
$$\begin{aligned} & F_{2}=F_{4}=F_{f}=\mu G / 2 \end{aligned}$$
(2)
According to the formula of (1), (2), the forces at different functional hand height were calculated, and the weight loads were added to the force points of the digital human model to analyze the forces on the lower back during different movements. The experimental animation collected data of LBA, NLA, and RZA at different movements.
Simulation predefined parameter analysis
Lower back analysis (LBA)
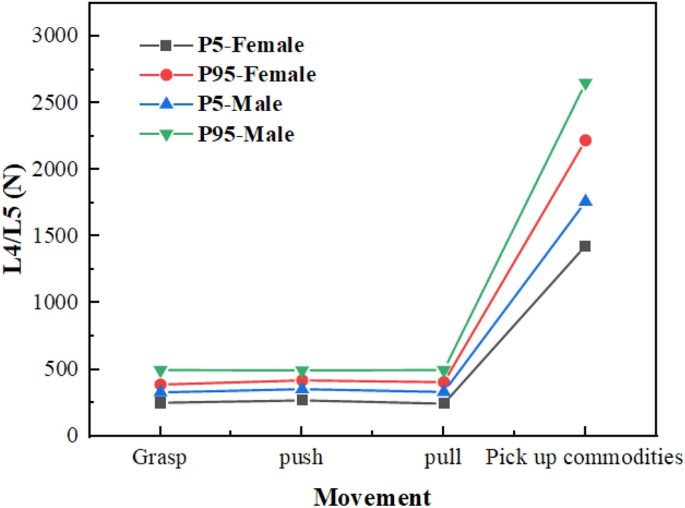
LBA helps you evaluate the spinal forces acting on a virtual human’s lower back, under any posture and loading condition. It assesses the forces on the L4/L5 lumbar spine when the virtual human is performing work22, To help guide the design in order to reduce the risk of injuries, and the L4/L5 position is shown in Fig. 7. The paper collects lower back pressure values based on existing shopping trolley for older adults during shopping activities such as grasping, pulling, pushing, and picking up commodities from the trolley. The likelihood of lower back injury increases with higher values. If the value exceeds 3400N proposed by NIOSH, there is a possibility of lower back disorders.
Based on the previous survey on shopping behavior among the elderly, it was found that users tend to pull the shopping trolley while shopping. This phenomenon is confirmed by simulation results, which show that pulling the shopping trolley puts less pressure compared with pushing on the lumbar spine. Different actions do not have a significant effect on the lower back pressure of different percentiles, but L4/L5 is higher for males than females at the same percentile. The lumbar pressures were within reasonable limits for all four maneuvers: grasping, pushing, pulling, and picking up commodities, as shown in Fig. 8.
NIOSH lifting analyses (NLA)
The NLA assesses the safe weight or load that can be lifted in a given position and time frame. Specifically, the Recommended Weight Limit (RWL) is the weight of the load nearly all healthy workers can be expected to handle over a reasonable period of time (not to exceed eight hours) without increasing the risk of developing lift-related low back pain. The lifting index (LI) is a relative estimate of the level of physical stress associated with a manual lifting task. The lifting index compares the actual weight of the load for a given task with the recommended weight. The greater the LI, the greater the risk of low back pain. The paper analyses five shopping processes in the pair shopping process. The NIOSH lifting equation are independent of height and weight parameters, resulting in identical simulation results for both male and female. The simulation results are presented in Table 2.
Based on the simulation analysis results, it is evident that each action’s LI1, which may increases the risk of LBP. RWL within the range from 10.41 kg to 12.15 kg.
Reach zones analysis (RZA)
The RZA tool describe the maximum and comfortable coverage area of the digital human, ensuring the target population has full access to the necessary components of the product to accomplish operational tasks more conveniently. To analyses the ease of access to commodities from the back of a shopping trolley for elderly individuals, using spherical data. The reachable domain analysis is conducted on P5 of females and P95 of males to validate the rationality of size the shopping trolley basket for the elderly.
According to the results (Fig. 9), the P95 of male and P5 of female are unable to reach products at the bottom of the shopping trolley when bending at \(60^{\circ }\) and \(30^{\circ }\) respectively. As a result, they have to remove products from the side or front of the trolley, which reduces shopping efficiency. The shortest straight-line distance from the floor was measured to be approximately 5100 mm using the ‘Measure Distance’ tool.
Optimization design
Man-machine size analysis
Using ergonomics as the theoretical basis, the NIOSH lifting equation’s variables were applied to the design of a senior shopping trolley. To limited the range of independent variable values and combined them with the constrained optimization method to obtain an optimal solution.
According to industrial designer Henry Dreyfuss, the most comfortable height for human body is 76 mm below the height of the human elbow. Therefore, the handle heights of shopping trolleys for male at the 5th, 50th, and 95th percentiles are 861 mm, 939 mm, and 1021 mm, respectively, respectively, the handle heights for female at the 5th, 50th, and 95th percentiles are 795 mm, 863 mm, and 934 mm, respectively. This means that the handle heights of shopping trolleys for senior citizens range from 795 mm to 1021 mm, which can be adjusted to three different levels: 795 mm, 908 mm, and 1021 mm, and the height of each gear is 113 mm, to feature caters to individuals with varying needs. The most comfortable grip diameter is between 30 mm and 40 mm, and an oval shape is preferred as it increases the contact area between the handle and the hand, providing better grip and support to the wrist. In addition, the shopping trolley’s width should not exceed the maximum shoulder width of the human body (377 mm), to improve portability of operations.
NIOSH lifting analysis (NLA)
The NIOSH lifting equation are determined LC, H, V, D, FM, A, and CM. The specific formulas, meanings, and value ranges for these argument are shown as formula (3), (4) and Table 3. Based on the survey of existing shopping trolleys, combines with the significance of the independent variables in the lifting equation is to limit value ranges.
$$\begin{aligned} & \textrm{RWL}=\textrm{LC} \times \frac{25}{H} \times (1-0.003|V-75|) \times \left( 0.82+\frac{4.5}{D}\right) \times (1-0.0032 \times A) \times F M \times C M \end{aligned}$$
(3)
$$\begin{aligned} & LI=\frac{Actual-task-load-weight}{RWL} \end{aligned}$$
(4)
Upon analysis of the formula, it is observed that when H and D take the minimum and V is 75, the RWL attains its maximum value, at the same time LI is minimized, using the constraint optimization method. Set the independent variable restriction conditions, so as to get in the case of RWL as large as possible, can allow the maximum volume conditions of the independent variable value, so that the space utilization of the elderly shopping trolleys to get the maximization of the results of the analysis as shown in Table 4.
Product function optimization
In design, it is essential to clarify the functional attributes of the product so that auxiliary functions serve the main function23. The handle and grip should be made of soft material with anti-slip properties, such as rubber or PU. The raised geometry of the palm area can reduce fatigue in the palm and wrist. Secondly, the elderly have relatively low physical mobility and hand strength. Therefore, the foot brake is more suitable for their needs. Additionally, anti-skid wheels maintain stability and grip on different surfaces, reducing unnecessary bumps and strain on the arms and lower back. Finally, a seat or cushion provides support and reduces fatigue when walking for long periods.
Comparison of LBA
When using a shopping trolley, elderly individuals are usually in an upright state during grasping, pushing and pulling, which reduces the risk of excessive force on the lower back. The paper employs LBA to analyze the action of picking up commodities from an optimized shopping trolley for the elderly. The L4/L5 forces before optimization are compared and analyzed, as shown in Fig. 10
The comparison demonstrates that the optimization can significantly decrease the force on the lower back. Specifically, the force can be reduced by approximately 600N in the most comfortable scenario and about 300N under the maximum volume scenario.
NIOSH analysis comparison
The LI, RWL and CLI of the two sizes, the most comfortable and the largest volume at the time of the five shopping trips were simulated and the simulated parameters were compared to validate the optimization results. The simulation Table 5 show that the CLI
Reachability analysis comparison
As shown in Fig. 11, after optimization, the shopping trolley allows the elderly to easily reach products at the bottom of the basket and retrieve them more conveniently. Additionally, the lowest handle position allows P5 of female to bend down \(60^{\circ }\), reducing the height of fingertips from the ground by 10cm and improving the shopping trolley’s convenience for the elderly.